Children's bodies are affected by parasites quite easily, as children have lower immunity. In addition, the child's body cannot produce a special digestive enzyme capable of destroying worm larvae; a person acquires this ability with age.
It is impossible to notice worm eggs visually; their size is microscopic, but they are present almost everywhere. The danger of infection arises in the period when the child begins to understand the world by feeling various objects. Moreover, the child strives not only to touch objects, but sometimes to taste them. Sandboxes in backyards, which are often used by street animals as toilets, pose a great danger. If we take into account the weak natural defense of the child's body against helminth infestations, it is not difficult to realize how high the chances are that the parasites will affect the child's intestines. Here are the main ways worms enter a child's body:
- through unwashed hands;
- after contact with animals;
- through undercooked meat and fish;
- insects are also often a source of helminth infestation, as they carry worm eggs on their legs;
- unwashed fruits and vegetables;
- through dirty water accidentally ingested while swimming in an open body of water.
An important factor is the ability of worms to be a source of reinfection of the child, despite all the efforts of the parents. The fact is that helminths periodically crawl through the child's anus, laying eggs in the immediate vicinity, which causes severe itching in the child. The child itches and small worm eggs, in turn, end up under his nails, from where they easily enter the mouth, and then travel along the gastrointestinal tract, ending up again in the intestine. After two weeks the larvae become adults, also capable of laying eggs.
Worm infestation in children, symptoms
There are about 300 types of parasites that can infect the human body, however, pinworms and roundworms are most often diagnosed in children. Both types of worms affect the small intestine; Symptoms of damage to both types of parasites are quite similar:
- Loss of appetite, pale facial skin, dark circles under the eyes.
- Restless sleep; sometimes the child may grind his teeth in his sleep.
- Headache, dizziness, lethargy and weakness appear.
- Sometimes worms are present in a child's stool and can be seen with the naked eye.
- The child feels itching in the genital area and anus.
- There is a disorder in the digestive system, constipation can be replaced by diarrhea, abdominal pain and nausea are observed.
- General indicators of blood count may change, namely a decrease in hemoglobin and an increase in the level of eosinophils and ESR.
- The vital activity of worms becomes the cause of general poisoning of the body, manifested in the appearance of allergic reactions, urticaria and atopic dermatitis.
- Increased body temperature for no good reason.
- Constant itching can cause inflammation of the genital mucosa.
- Worms not only poison the child's body with the products of their vital activity, but also actively consume vitamins and minerals, nutrients that the child's body needs so much, which often leads to vitamin deficiency and decreased hemoglobin level in the blood.
Folk remedies against worms
It is true that folk remedies are most suitable for treating helminth infestations in children; the symptoms regress quite quickly. However, before using them, you must definitely consult a doctor, because the child's body is very vulnerable not only to the action of parasites, but also to inept use of medicines, even popular ones. Here are the most popular folk anthelmintic remedies:
- Garlic enema. Garlic is an antiseptic given to man by nature; it is also applicable against worms. A glass of cow's milk is mixed with a chopped head of garlic, the mixture is boiled, then cooled and filtered through a double layer of gauze. At night, the child is given an enema from the received milk, a third of the received drug is taken, and the child is treated in this way for at least a week.
- Chamomile decoction. Another natural antiseptic used to treat a wide variety of diseases. To prepare the decoction, take a spoonful of dry chamomile herb and pour boiling water over it, let it cool and give the child to drink during the day instead of water or tea. The duration of treatment is 5 days.
- Onion remedy. Chop a small onion, add the milk and boil the resulting mixture, then cool and filter. The resulting product is administered to the child for three consecutive days, 100 ml.
Simple folk recipes that will help cure a child from worms, see the video:
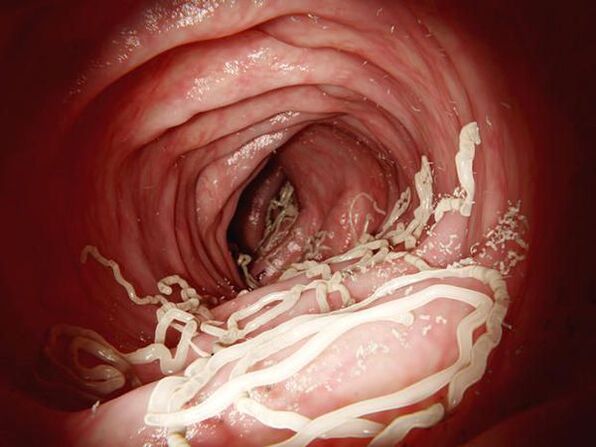
Causes of helminthiasis
Almost 400 species of helminths can parasitize the human body, 70 of these are the most widespread in our country. As a rule, these are roundworms and tapeworms. Often, diseases caused by the penetration of trematodes (feline or liver flukes) are detected.
The disease develops when eggs or larvae of parasites enter the stomach. During the period of development from the egg to the sexually mature individual, tapeworms can change several hosts. You can also become infected by eating meat (beef, pork, game), unfiltered water, dirty fruits and vegetables.
Helminths parasitize mammalian, fish, mollusc and amphibian organisms. To avoid contagion, you must avoid eating them raw and do not buy smoked or salted fish of unknown origin.
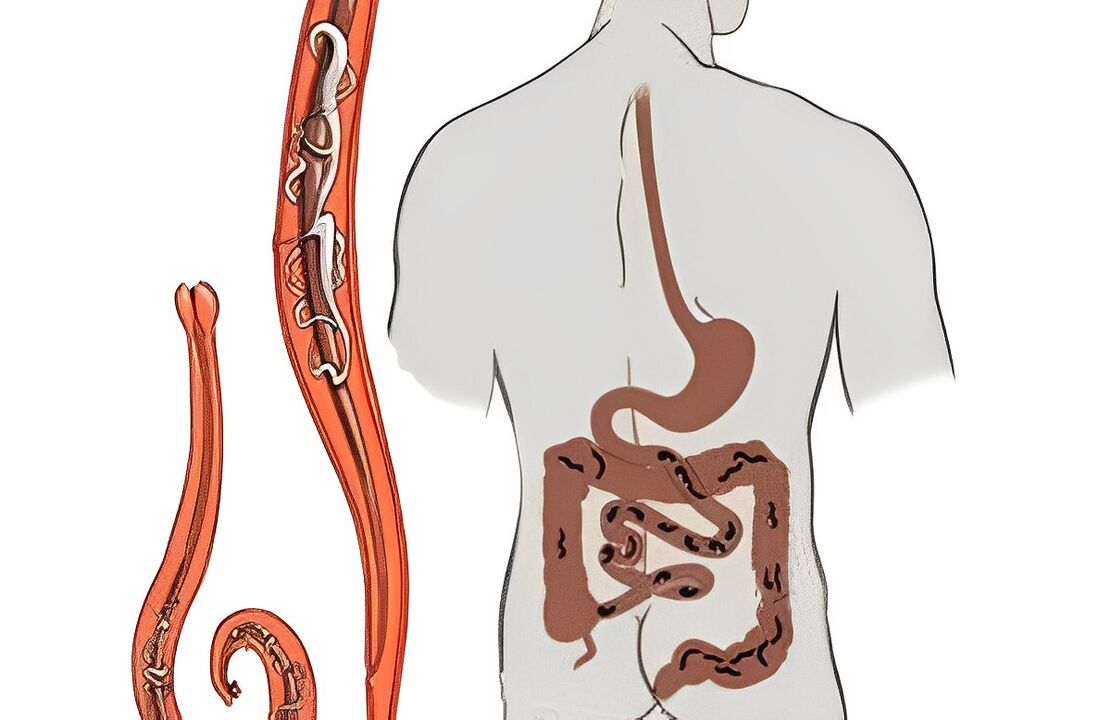
Symptoms of worms
Various types of worms can parasitize the digestive tract, respiratory organs, lymph nodes, bone and muscle tissues. Their vital activity affects the host's body in different ways. They can produce toxins, cause the development of inflammatory processes, allergic reactions, anemia, metabolic disorders and have a traumatic effect on organs and tissues.
You should contact the clinic to identify or exclude helminthiasis if you have the following symptoms in an adult:
- Temperature increase. It can rise sharply to 38°C and decrease briefly after taking anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs. Sometimes the temperature remains high for 2-3 months.
- Dull or sharp pain in the stomach, frequent bowel movements (diarrhea or constipation), nausea.
- Itching in the anal area, worse in the evening.
- Frequent colds or respiratory diseases: when infected with helminths, immunity decreases.
- Loss or increase in appetite, sudden loss of body weight.
- Bronchospasms, cough, shortness of breath, other respiratory disorders, paleness of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Itchy skin rash.
- Insomnia, frequent headaches, anxiety, irritability, depression.
- Joint and muscle pain.
- Inflammation, swollen lymph nodes.
- Edema.
In the absence of adequate treatment, helminths can provoke the development of chronic pancreatitis, hepatitis, cholecystocholangitis, cause irreversible changes in tissues and even lead to death.
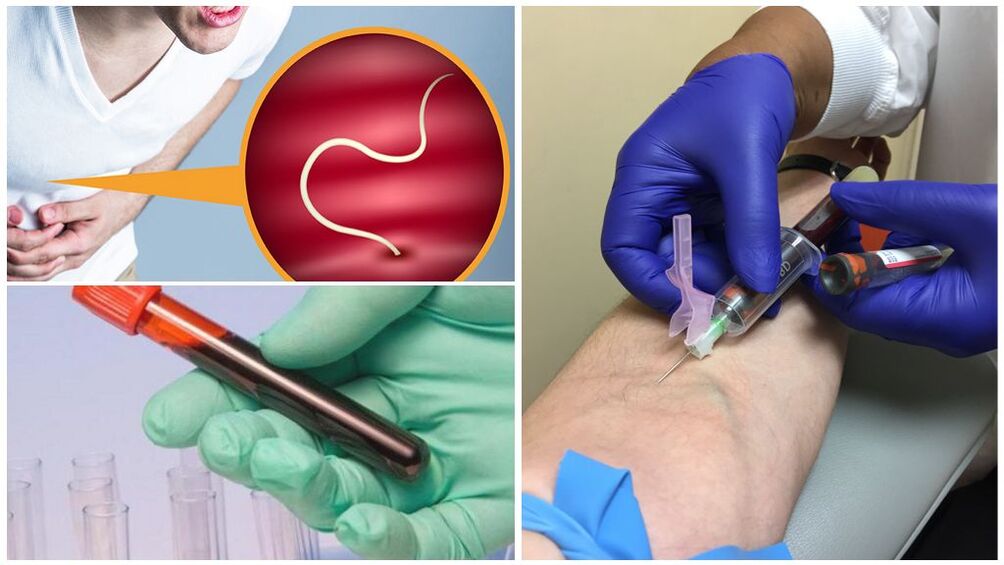
Diagnostics
Infection with some types of helminths gives a characteristic clinical picture. When a patient first contacts a doctor, she can guess the diagnosis. During the examination of feces, eggs and other traces of the vital activity of roundworms, pinworms and other roundworms parasitizing the intestine are detected. Sometimes worms are visible on ultrasound. But some small parasites are very difficult to identify. The diagnosis is made based on a combination of symptoms and results of instrumental and laboratory tests.
If helminthiasis is suspected in adults and children, the following should be taken:
- Stool analysis. It allows you to accurately detect the presence of common parasites in the body. However, some of them only lay eggs at certain stages of their life cycle, so it is recommended to carry out surveys several times at intervals of 3-4 days.
- General clinical blood test. It does not indicate the presence of larvae, eggs, adults, but provides a lot of information about the intensity of the inflammatory process, the number of leukocytes, etc.
- Biochemical analysis. It provides detailed information on protein metabolism, identifies abnormal loss or increase in protein synthesis, and allows infection with certain helminths to be ruled out or suspected.
- Analysis of liver function indicators (bilirubin, pancreatic alpha-amylase, alkaline phosphatase, AST, ALT). Diagnosis of the liver and pancreas suggests helminth infection.
- Urinalysis, blood test with glomerular filtration. They provide the doctor with information about the state of the kidneys and the possibility of them being damaged by parasites.
Studies of bile, sputum and duodenal contents may also be prescribed.
To clarify the localization of parasites and assess the extent of damage, ultrasound diagnostics may be prescribed. If the presence of helminths in the brain or eyes is suspected, a computed tomography scan is performed. To diagnose helminths in the lungs, X-rays are performed, and in the stomach and intestines - endoscopy.
A comprehensive examination allows you to quickly and accurately determine the causes of the disease and prescribe adequate treatment. Don't refuse the exam. The more accurately the doctor determines the cause of poor health, the faster he will be able to help.
Which doctors should I contact?
If you suspect a helminth infection, you should contact a therapist who will carry out an initial examination and prescribe laboratory and instrumental tests. After the examination, your therapist will prescribe treatment or refer you to a specialist doctor.
Treatment
With timely diagnosis, helminthiasis can be easily eliminated with the help of anthelmintic drugs. The doctor determines the dosage based on the patient's age, weight, degree of parasitic damage, type and location. To get rid of most worms, it is enough to take the drug 1-3 times. Along with anthelmintic drugs, vitamin and mineral complexes are often prescribed to strengthen the immune system.
In case of severe intoxication, allergic reactions, infection against the background of serious chronic diseases, hospitalization may be required. Doctors will not only rid the human body of parasites, but also carry out detoxification therapies and vitamin therapies.
Surgical treatment is necessary for helminth damage to organs and tissues. Large numbers of roundworms sometimes lead to obstruction of the intestines and bile ducts. Their accumulation is surgically removed. The decision on the need for surgical treatment is made by the doctor after a thorough examination. The complexity and duration of the operation depends on the location of the parasites, their size and quantity.
Complications
Heartworm infections caused by common types of parasites can be treated with medications prescribed by your doctor. But if you do not pay attention to the alarming symptoms, deterioration of health, weakness, causeless fatigue, decreased immunity, the disease can lead to serious complications.
If the parasites enter the lungs and the patient does not consult a doctor, cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, difficulty breathing, pneumonia or even bronchial asthma may develop.
Parasites in the digestive organs can cause cirrhosis, liver abscess, hepatitis, intestinal cancer, gastrointestinal bleeding, accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites), and peritonitis. They also often cause the development of chronic kidney disease, meningoencephalitis, and vision loss. Some tapeworms (tapeworms) grow more than 1 meter long, and the small roundworms can form dense balls. This disrupts the normal functioning of the body, leading to severe intoxication and severe allergic reactions. Without urgent medical attention, death is possible.
Classification of parasites
Different types of worms affect the body differently and have their own characteristics both in the development cycle and in the appearance and damage caused. There are three most common groups of worms: roundworms, tapeworms and trematodes.
The first group is the protocavitary worms. They live in soil and water, so they can easily become infected in the sandbox and during a walk in general. It is this group that includes the most common pinworms and roundworms, and also includes hookworms, trichinae, and guinea worms. Depending on the parasite that caused the infection, ascariasis, enterobiasis, trichuriasis, etc. are distinguished.
Cestodoses are tapeworms that can live both in the intestine (the most common variant are tapeworms) and in organs (usually the larvae of tapeworms, echinococci and alveococci live there). Depending on which of these types of worms are found in children, echinococcosis, taeniasis, hymenolepiasis, etc. are distinguished.
And the last of the three popular groups are flukes caused by flukes. These are different types of flatworms: schistosome, cat/liver fluke, leucochloride. They cause opisthorchiasis (transmitted by fish of the carp family) and fascioliasis (affect the liver and biliary system, infection through plants or water).
Symptoms
There are many symptoms, and individual manifestations depend on which helminth eggs have entered the body. Next we will talk about the general symptoms of all parasitic infections, then enterobiasis, ascariasis and 5 other types of infections.
- increased irritability, restless sleep, decreased perseverance and attention, frequent hysterics and anger;
- increased appetite associated with active weight loss;
- symptoms of the digestive system: diarrhea, constipation, nausea, pain in the right hypochondrium;
- dizziness and headache;
- food allergy;
- nasal discharge;
- diseases and infections of the reproductive system;
- brittle nails/hair;
Enterobiasis is a helminthiasis in which the body is infected with pinworms. The larvae emerge from the eggs within 4-6 hours; in 2-4 weeks they become adults: greyish or white nematodes 5-10 mm long. They settle in the cecum and appendix and lay their eggs outside the anus: at night the female pinworms come out into the air for this purpose. This reproduction mechanism leads to severe nocturnal itching, resulting in restless sleep, tossing and turning and screaming.
Additional special symptoms:
- nocturnal urination;
- grinding of teeth;
Ascariasis is a helminthiasis in which the body is colonized by roundworms. These worms are already larger: the average length of an adult is 25-30 cm. The larvae and eggs enter the body with insufficiently disinfected fresh fruits and vegetables. The development period takes place in the intestine, after which they pass into the lymphatic and blood vessels and, with the flow of blood and lymph, are distributed throughout the body: in the liver, heart, lungs. They then enter the oral cavity and are swallowed again. From this moment adult nematodes begin to develop. This takes approximately 3 months.
How to suspect the presence of worms in children:
- the liver, spleen, lymph nodes enlarge;
- the temperature rises, sometimes up to 38 degrees;
- malaise and weakness appear;
- respiratory pathologies develop: pneumonia, bronchitis and bronchial asthma;
- load losses;
- Gastrointestinal symptoms appear: constipation, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, pain in the form of contractions;
- fear of light;
- night terrors;
- dry cough - sputum with an orange tint and bloody spots.
It is more difficult to breed roundworms than pinworms, since the female lays almost 250 thousand eggs every day. In no case should you rely on traditional methods or buy the first remedy you come across in the pharmacy - be sure to contact a specialist.
Newborns may show symptoms as early as a few weeks of life if they have received worm eggs and larvae from their mother, for example during childbirth. As a rule, symptoms are manifested in the form of failure to gain weight, excessive drooling, rash, paleness, blueness under the eyes, constipation. The child is constantly worried, screams, sleeps and eats poorly. The screaming can be unbearable and the child will turn blue in the process.
Worms are often the cause of the development of lung pathologies and are diagnosed using ultrasound or X-rays. Parasites, especially the tapeworm Echinococcus, can damage not only the respiratory system, but also travel further to the brain and heart. In the areas where helminths develop in the lungs, scars and adhesions appear, and the shape of the lungs begins to change. Such changes cause a wide range of diseases: asthma, fibrosis, bronchitis, pleurisy, emphysema, etc. When a tapeworm enters the lungs, echinococcosis is formed, when the parasite develops in the form of a cyst.
Symptoms will largely depend on which helminth has entered the body, but the child's anxiety and the presence of the above general symptoms should alert parents. If signs of worms appear, make an appointment with a pediatrician or gastroenterologist to get tested in a timely manner.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of worms in children is carried out in different ways: depending on the worms with which the child is infected, the habitat, location of the eggs and toxins present in the body will be different.
To make a diagnosis, the following may be prescribed:
- blood test: shows levels of anemia, hemoglobin and eosinophils;
- parasite analysis - in 99% of cases helps to detect helminthiasis and in most cases helps to accurately determine the type (biomaterial for research - blood from a vein);
- stool examination - there may be no eggs in the stool, even if there is an infection, to ensure the presence of worms, this diagnosis should be carried out 3 times, which takes time;
- smear - especially effective in case of infection with pinworms, since their eggs are located just outside the anus;
- stool analysis for dysbacteriosis;
- if there is suspicion of infection of the internal organs and not just the gastrointestinal tract: CT, x-ray, ultrasound.
Diagnostics allows you to accurately identify the type of parasite and prescribe specific treatment. The doctor prescribes medications, diet, additional supportive procedures and gives recommendations for care and hygiene.
In some cases, parents pay increased attention to helminthiasis and are constantly worried about infecting their child. This leads to regular "preventive" courses of serious anthelmintic drugs, which do not bring any benefit to the child's body. If your child is not losing weight, feels well, eats well, has a healthy complexion and is not itching in the anal area, he is probably healthy. If you want to be sure, it's better to take the test than take an unnecessary course.
Treatment
The course of therapy for worms in children includes several stages: preparation, therapy and cleaning. During the entire treatment it is necessary to carry out general preventive measures and carefully observe hygiene to avoid reinfection or infection of one of the family members. Some types of worms, such as tapeworms and echinococci, can only be removed by surgery.
The preparatory stage involves taking various sorbents that absorb toxins and cleanse the body. Antihistamines follow, they relieve general itching and prevent the development of allergic reactions to drugs.
Treatment of helminthiasis in children in the main stage consists in direct intake of anthelmintic drugs in the form of tablets, suppositories or suspensions. Drugs are selected based on the type of helminths, individual indications and contraindications. Some anthelmintics work in 2 doses:
- the first kills already developed individuals;
- the second course helps to cope with larvae and eggs (prescribed 2 weeks after the first).
Cleansing is designed to rid the body of the remains of dead parasites, at this stage sorbents, enemas and choleretic drugs are used. You can help your child by adding raw carrots, dairy products, coarse bread, fruits, vegetables, fish oil, nuts, especially walnuts and peanuts, to the diet.
Also, to restore the body in case of serious damage, vitamin complexes, iron, minerals and a special diet can be used, which will increase hemoglobin, restore liver function and strengthen the body as a whole. The doctor describes the treatment plan in detail, avoiding side effects. Control tests are necessary. Self-medication and deviations from the plan are not allowed.
Consequences of untreated parasitic infestations
Helminthiasis represents a serious danger; without treatment it can cause death or serious health problems. An infected child represents a danger to the entire family and the environment as he spreads the disease.
Complications of Worms in Children:
- inflammatory exacerbation of appendicitis;
- Seizures;
- visual impairment of different types;
- allergic reactions with abundant nasal discharge;
- developmental delay compared to peers;
- sexually transmitted infections, the most common in girls is vulvovaginitis;
- various types of pulmonary manifestations, including bronchial asthma;
- in difficult cases: damage to the brain and heart.
Prevention
To ensure that treatment of worms in children is not necessary at all, it is necessary to actively engage in prevention, which consists of both daily precautions and hygiene procedures, as well as taking medications.
How to protect your baby from parasitic infections:
- Maintain hygiene: wash your child's hands regularly and bathe;
- regularly care for toys - washing and cleaning (after diagnosis, all toys must be disinfected);
- cut your nails as often as possible, clean them every day;
- iron clothes after washing;
- get rid of bad habits: sucking fingers, pens, biting nails;
- give only boiled water to drink and explain the reasons;
- avoid swimming in natural bodies of water;
- use repellents (insects often carry worm eggs), destroy all insects that enter the house;
- regularly check pets for parasites;
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly, carry out sufficient heat treatment of meat and fish.
Some types of helminthiasis are difficult to cure, so we recommend preventive measures to avoid infection. By contacting the clinic, parents will receive comprehensive advice on how to properly carry out prevention to avoid problems in the future.